Dental care Treatments
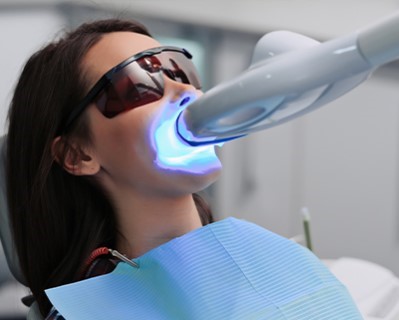
Teeth Whitening
- Purpose: Enhances the brightness of teeth by removing stains and discoloration.
- Procedure: Bleaching agents such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide are applied to the teeth.
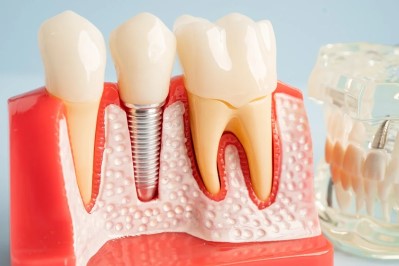
Dental Implants
Purpose: To replace missing or damaged teeth with fixed alternatives to improve the function and aesthetic appearance of the mouth. Dental implants are secured in the jaw using metal screws that act as the roots for artificial teeth.
Procedure: The dental implant process involves placing metal screws, usually made of titanium, into the jawbone. After a healing period known as "osseointegration," an artificial crown or bridge is attached to these screws to restore the function of natural teeth.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Dental implants are typically performed as an outpatient procedure. It can be completed during a visit to the dental clinic or in several stages depending on the complexity of the case.
Duration of Hospital Stay: Patients usually do not require hospitalization. The implant procedure is done in the clinic, and patients may need follow-up visits after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: Dental implants are usually performed under local anesthesia, which aims to numb the area around the implant. In some cases, general anesthesia or sedation may be used if the procedure is more complex.
Travel After Procedure: Patients are advised to avoid long-distance travel immediately after the implant procedure, especially in the first few days, to allow the area to heal and monitor any potential complications such as pain or swelling.
Preparation Before Procedure: Preparing for dental implants requires comprehensive examinations of the mouth and teeth, including X-rays to ensure there is enough bone to support the implant. Patients may also be asked to stop taking certain medications that could affect the healing process.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of the dental implant procedure varies based on the number of implants and the technical complexity of the operation, but it typically takes 2 to 3 hours. The procedure involves placing the metal screws in the jaw, followed by a waiting period of several months for healing and osseointegration before attaching the final crown or bridge.
Recovery Time: Recovery from dental implants may take several months. This includes an initial healing period after the implant, which may take 1 to 2 weeks, followed by a longer healing period during which osseointegration occurs, potentially taking 3 to 6 months before the final crown is attached.
Estimated Cost: The cost of dental implants varies based on the number of implants, type of materials used, the dentist's expertise, and geographical location. Dental implants can be relatively expensive, and patients should consult with their dentist or clinic for detailed information about costs.
Post-Procedure Care: After dental implants, it is essential to follow the dentist's instructions regarding implant care and oral hygiene. This includes regular tooth brushing, using dental floss, and avoiding hard or sticky foods during the healing period. Patients should also attend all follow-up appointments to ensure the success of the implant and assess oral health.
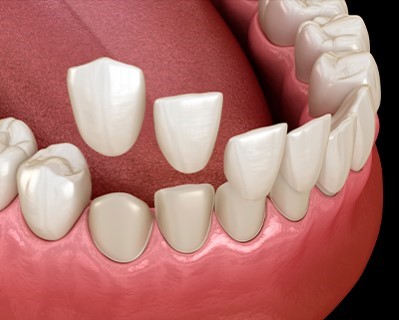
Veneers
Purpose: Veneers are used to improve the appearance of teeth by covering imperfections such as discoloration, chips, gaps, or misalignment. They provide a natural-looking aesthetic improvement by bonding thin shells to the front surface of teeth.
Procedure: Veneers involve placing custom-made, thin shells, usually made from porcelain or composite resin, onto the front side of the teeth. This process often requires removing a small amount of enamel from the teeth to ensure the veneers fit properly and look natural.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Veneers are typically placed during an outpatient visit to the dental clinic. The procedure usually takes place over two or more appointments depending on the number of veneers and the complexity of the case.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required for veneers. Patients typically visit the clinic for the procedure and can go home the same day.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia may be used to numb the area where enamel is being removed from the teeth. However, some cases may not require any anesthesia if minimal enamel removal is needed.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel after the procedure without significant restrictions. However, it’s advisable to allow a short period of recovery, especially if anesthesia was used, to ensure there is no discomfort.
Preparation Before Procedure: The preparation for veneers usually includes a thorough dental examination and X-rays to ensure that veneers are a suitable option. The dentist may also take impressions of the teeth to create custom veneers that fit perfectly.
Duration of Procedure: The process of placing veneers typically takes one to two hours per session. If multiple veneers are being placed, it may take additional appointments. The procedure includes preparing the teeth, creating impressions, and bonding the veneers to the teeth.
Recovery Time: Recovery from veneer placement is usually quick, with many patients returning to normal activities the same day. Minor sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures may be experienced in the days following the procedure but should subside.
Estimated Cost: The cost of veneers varies based on the material used, the number of teeth being treated, and the dentist's expertise. Porcelain veneers are typically more expensive than composite veneers. Patients should consult with their dentist or clinic for a detailed cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After getting veneers, patients should follow good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing. It is also important to avoid biting on hard objects like ice or pens, as this could damage the veneers. Regular dental checkups should be maintained to ensure the long-term success of the veneers.
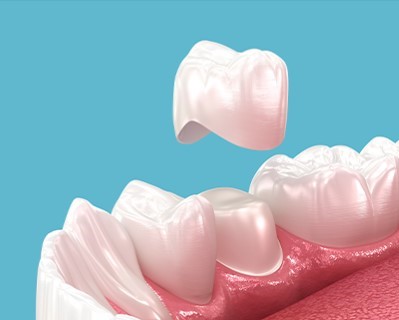
Dental Crowns
Purpose: Dental crowns are used to restore the shape, size, and strength of a damaged or decayed tooth. They are placed over the tooth to improve its appearance and function, protecting the underlying structure and preventing further damage.
Procedure: A dental crown is a cap made from materials like porcelain, ceramic, metal, or a combination, which is placed over a damaged tooth. The tooth is reshaped and reduced to fit the crown, then the crown is custom-made and cemented in place to restore the tooth’s function and appearance.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Dental crowns are typically placed in an outpatient dental visit. The procedure usually takes place over two appointments—one for preparation and one for placement of the crown.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required for dental crowns. Patients can leave the clinic the same day after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is usually used to numb the tooth and surrounding area during the procedure, making it comfortable for the patient.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel without restrictions after the procedure. It’s recommended to wait for the numbness to wear off and ensure there are no immediate complications.
Preparation Before Procedure: Preparation involves examining the tooth, taking X-rays, and sometimes performing a root canal if the tooth is badly damaged. The dentist will take an impression of the tooth to create a custom-fit crown.
Duration of Procedure: The process of placing a dental crown typically takes two appointments. The first visit (for preparation and impressions) may take 60 to 90 minutes. The second visit (for crown placement) is usually shorter and involves cementing the crown in place.
Recovery Time: Recovery from a dental crown procedure is usually quick. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or sensitivity for a few days, but normal activities can usually be resumed immediately after the procedure.
Estimated Cost: The cost of a dental crown varies based on the material used, the complexity of the procedure, and geographical location. Porcelain and ceramic crowns tend to be more expensive than metal crowns. Patients should consult with their dentist for a detailed cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After receiving a dental crown, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing. Avoid chewing on hard objects like ice or pens, which could damage the crown. Regular dental checkups are essential to monitor the health of the crown and the surrounding teeth.
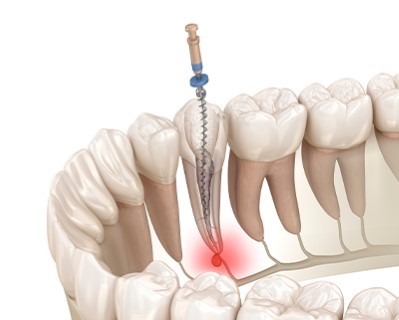
Root Canal Treatment
Purpose: A root canal is performed to save a severely damaged or infected tooth by removing the infected or inflamed pulp tissue from inside the tooth. The procedure prevents further infection and relieves pain, restoring the tooth's function without needing extraction.
Procedure: The dentist or endodontist drills into the tooth to access the infected pulp tissue in the root canals. The pulp is then removed, and the inside of the tooth is cleaned, disinfected, and sealed with a filling. In some cases, a crown is placed over the tooth for added protection.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Root canal treatment is typically done in a dental clinic as an outpatient procedure. The process is completed in one or two visits, depending on the severity of the infection.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is needed for a root canal. Patients can go home after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used to numb the area around the affected tooth, ensuring the patient does not feel pain during the procedure. In some cases, sedation may be offered for anxious patients.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel after a root canal without any significant restrictions. It is recommended to avoid eating or drinking until the numbness from the anesthesia wears off to prevent injury to the mouth.
Preparation Before Procedure: Preparation for a root canal includes an examination and X-rays to assess the extent of the infection and to determine the shape of the root canals. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed before the procedure to manage infection.
Duration of Procedure: The root canal procedure usually takes about 60 to 90 minutes per session. The time varies depending on the complexity of the tooth’s root structure and the extent of the infection. Some cases may require two appointments to complete.
Recovery Time: Recovery from a root canal is generally quick, with most patients experiencing mild discomfort or sensitivity for a few days. Over-the-counter pain relief medications are usually sufficient to manage any discomfort. Normal activities can typically be resumed the day after the procedure.
Estimated Cost: The cost of root canal treatment depends on the tooth involved (molars are more complex and costly than front teeth), the dentist's expertise, and geographical location. Patients should consult their dentist for a detailed cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After a root canal, patients should maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly. A follow-up appointment may be required to place a crown or permanent filling on the tooth. Avoid chewing on hard foods with the treated tooth until it is fully restored to prevent fractures.
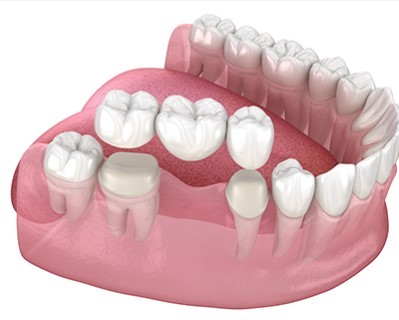
Dental Bridges
Purpose: Dental bridges are used to replace one or more missing teeth by "bridging" the gap between existing teeth. A bridge improves chewing, speech, and overall aesthetics, and prevents surrounding teeth from shifting out of position.
Procedure: A dental bridge typically consists of one or more artificial teeth (pontics) anchored to neighboring natural teeth or implants (abutment teeth). The abutment teeth are prepared by reshaping them and placing crowns, which hold the bridge in place. In cases of implant-supported bridges, the bridge is anchored directly to dental implants.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Dental bridges are placed during an outpatient visit to the dental clinic. The process typically involves two or more appointments: one for preparation and impressions, and another for fitting and cementing the bridge.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required for dental bridges. Patients can go home after each visit.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is usually applied to numb the area where the abutment teeth are prepared. In cases where implants are involved, sedation may also be used.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel after each session of the dental bridge procedure. It’s advisable to wait until the numbness from the anesthesia wears off before eating or drinking.
Preparation Before Procedure: Preparation involves a thorough examination and X-rays of the teeth and jaw to assess the best approach for placing the bridge. Impressions of the teeth are taken to ensure the bridge is custom-made to fit properly.
Duration of Procedure: The process of placing a dental bridge usually requires two appointments. The first visit, which involves preparing the abutment teeth and taking impressions, can take about 1 to 2 hours. The second visit, where the bridge is placed, usually takes less time.
Recovery Time: Recovery after getting a dental bridge is generally short, with some patients experiencing mild discomfort or sensitivity. Any discomfort typically subsides after a few days, and patients can resume their normal activities almost immediately.
Estimated Cost: The cost of a dental bridge varies depending on the number of teeth being replaced, the materials used (porcelain, metal, or a combination), and the location. Bridges supported by implants are generally more expensive. Patients should consult their dentist for a detailed cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After receiving a dental bridge, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly, particularly around the bridge. Special flossing tools may be needed to clean under the bridge. Regular dental checkups are essential to monitor the bridge and surrounding teeth.
_20240719135310943674__0.webp)
Orthodontic Treatment (Braces)
Purpose: Orthodontic treatment with braces is used to correct misaligned teeth, crowded teeth, or issues with bite (overbite, underbite, crossbite). It improves the function, health, and appearance of teeth, providing a better smile and reducing the risk of dental issues such as tooth decay or gum disease.
Procedure: Braces consist of brackets that are attached to the teeth and connected by wires, which are gradually tightened over time to move the teeth into the desired position. There are different types of braces, including metal, ceramic, lingual braces, and clear aligners. The treatment plan is customized based on the individual’s dental needs.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Braces are placed during an outpatient visit to the orthodontist. The process involves multiple visits over the course of the treatment, with adjustments made every few weeks.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required for braces. Patients can go home after each appointment.
Type of Anesthesia: No anesthesia is usually needed for placing braces. In rare cases, local anesthesia may be used if any tooth extraction is required prior to treatment.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel without restrictions after each session. There may be some discomfort or soreness after adjustments, but this generally does not affect normal activities.
Preparation Before Procedure: The orthodontist will perform a thorough dental examination, take X-rays, and create a treatment plan. Impressions or digital scans of the teeth are taken to custom-make the braces or aligners. In some cases, teeth may need to be extracted to make space for proper alignment.
Duration of Procedure: The initial placement of braces can take 1 to 2 hours. Follow-up visits for adjustments or tightening usually take 30 minutes to 1 hour. The overall duration of orthodontic treatment can range from 18 months to 3 years, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery Time: After each adjustment, patients may experience mild discomfort or soreness for a few days. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage this. Eating soft foods for a day or two after adjustments is often recommended.
Estimated Cost: The cost of orthodontic treatment varies depending on the type of braces, the complexity of the case, and the length of treatment. Traditional metal braces tend to be more affordable, while clear aligners and ceramic braces are often more expensive. Patients should consult their orthodontist for a detailed cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: Proper oral hygiene is essential during orthodontic treatment. Patients should brush and floss regularly, and may need special cleaning tools to keep braces and wires clean. Avoiding hard or sticky foods that could damage the braces is important. Regular visits to the orthodontist are required for adjustments and monitoring progress.
Dental Bonding
Purpose: Dental bonding is used to repair chipped, cracked, or discolored teeth, close gaps between teeth, or change the shape of teeth. It improves the appearance of teeth and can also be used to protect exposed roots of teeth due to gum recession.
Procedure: During dental bonding, a tooth-colored resin material is applied to the tooth and then hardened using a special light. The resin is shaped and polished to match the rest of the teeth. This procedure is minimally invasive and usually does not require anesthesia unless it is being used to fill a cavity.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Dental bonding is done in the dentist's office during an outpatient visit. The procedure typically takes one visit.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required for dental bonding. Patients can go home immediately after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: In most cases, no anesthesia is needed for dental bonding unless it is being used to fill a decayed tooth. Local anesthesia may be applied if necessary.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel immediately after the procedure, as there are no significant restrictions following dental bonding.
Preparation Before Procedure: Very little preparation is needed for dental bonding. The dentist will select a shade of resin that matches the patient's natural teeth. No significant tooth alteration is required.
Duration of Procedure: The procedure usually takes 30 minutes to 1 hour per tooth, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery Time: There is no downtime after dental bonding. Patients can resume their normal activities right away. Some may experience minor tooth sensitivity after the procedure, but it usually subsides within a few days.
Estimated Cost: The cost of dental bonding varies depending on the number of teeth being treated and the complexity of the procedure. It is generally considered one of the more affordable cosmetic dental procedures.
Post-Procedure Care: After dental bonding, it's important to maintain good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing regularly. Patients should avoid habits such as biting nails or chewing on hard objects, as the bonding material can chip. Additionally, avoiding staining foods and drinks (such as coffee and wine) in the first 48 hours can help maintain the appearance of the bonding.

Tooth Extraction
Purpose: Tooth extraction is the removal of a tooth that is damaged, decayed, or causing overcrowding in the mouth. It may be necessary if a tooth cannot be repaired with a filling, crown, or other treatment, or to prepare for orthodontic work, such as braces, or the removal of impacted wisdom teeth.
Procedure: During tooth extraction, the dentist or oral surgeon loosens the tooth in its socket using special instruments, then carefully removes it. For simple extractions, only local anesthesia is needed, while surgical extractions, such as removing impacted teeth, may require stitches and additional care.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Tooth extraction is typically performed in a dentist's or oral surgeon's office as an outpatient procedure. In rare cases of surgical extraction, the patient may need to visit an oral surgery center.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Patients can go home shortly after the procedure once the anesthesia wears off.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used for simple extractions to numb the area around the tooth. For more complicated extractions, such as wisdom teeth removal, the dentist may also use sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the case and patient comfort.
Travel After Procedure: Patients are generally advised not to drive or travel for a few hours after the procedure if sedation or general anesthesia was used. After simple extractions with local anesthesia, patients can usually travel immediately, but should avoid strenuous activity for the remainder of the day.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before tooth extraction, the dentist will take X-rays of the tooth and surrounding area to plan the extraction. Patients may need to stop taking certain medications that could affect healing. It's also important to discuss any medical conditions that might affect the procedure or recovery.
Duration of Procedure: Simple extractions usually take around 20 to 40 minutes. Surgical extractions may take longer, especially if the tooth is impacted or broken. The entire visit may last an hour or more, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery Time: Recovery from a tooth extraction generally takes a few days. Patients may experience some pain, swelling, or minor bleeding in the first 24 to 48 hours. Full healing of the gum can take several weeks. Patients are advised to avoid smoking, spitting, and drinking through a straw for at least 24 hours to prevent dry socket, a painful condition where the blood clot in the extraction site is dislodged.
Estimated Cost: The cost of tooth extraction varies depending on whether it is a simple or surgical extraction, the location of the tooth, and the complexity of the procedure. Surgical extractions, such as those for impacted wisdom teeth, tend to be more expensive. Patients should consult their dentist or oral surgeon for an exact cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After tooth extraction, patients should follow the dentist's instructions for pain relief, which may include over-the-counter pain medications or prescribed drugs. It’s important to keep the extraction site clean by gently rinsing the mouth with salt water after 24 hours, avoiding vigorous rinsing. Soft foods are recommended during the initial recovery period. Patients should also attend any follow-up appointments to monitor healing.

Gum Contouring
Purpose: Gum contouring is a cosmetic dental procedure that reshapes the gum line to improve the appearance of the smile. It is often performed to correct a “gummy smile,” where excessive gum tissue is visible when smiling, or to create a more balanced and aesthetically pleasing gum line.
Procedure: During gum contouring, a dentist or periodontist uses a laser or surgical scalpel to remove excess gum tissue. The procedure may involve numbing the area with local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort. The gums are then carefully reshaped to create a more harmonious balance with the teeth.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Gum contouring is usually performed in a dental office as an outpatient procedure. It typically takes about an hour or less, depending on the extent of the contouring needed.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Patients can return home immediately after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is typically used to numb the area being treated. In some cases, sedation may be offered to help patients feel more relaxed during the procedure.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel home immediately after gum contouring. It's advisable to avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day, especially if sedation was used.
Preparation Before Procedure: Prior to gum contouring, patients may undergo a dental examination and X-rays to assess the gum tissue and plan the procedure. It is important to discuss any medications being taken and to maintain good oral hygiene leading up to the appointment.
Duration of Procedure: The gum contouring procedure usually takes 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the complexity and extent of reshaping required.
Recovery Time: Recovery from gum contouring typically takes about a week. Patients may experience mild swelling and discomfort, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relief. It's important to follow post-operative care instructions, including soft food consumption and avoiding vigorous brushing around the treated area.
Estimated Cost: The cost of gum contouring varies based on the complexity of the case and the dentist's fees. On average, it can range from a few hundred to a couple of thousand dollars. Patients should consult their dentist for a detailed estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial. Patients should follow any specific care instructions provided by their dentist, such as avoiding certain foods and using a gentle mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups are recommended to monitor gum health.
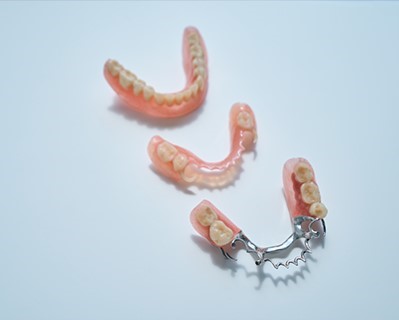
Dentures
Purpose: Dentures are removable prosthetic devices designed to replace missing teeth and restore function and aesthetics to the mouth. They help improve chewing ability, speech, and facial appearance, while also providing support to the surrounding soft tissues.
Procedure: The process of getting dentures typically involves several appointments. First, the dentist conducts an oral examination and takes impressions of the mouth to create a custom-fit denture. The dentist may also extract any remaining teeth if necessary. Once the dentures are made, they are fitted and adjusted for comfort and functionality.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Dentures are usually fitted and adjusted in a dental office as an outpatient procedure. There may be multiple visits required, but no overnight hospital stay is necessary.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Patients can return home after each appointment.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia may be used during tooth extractions if necessary, but dentures themselves do not require anesthesia during fitting.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can travel immediately after their denture fitting appointments. However, it is advisable to avoid long trips until they feel comfortable with their new dentures.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before getting dentures, patients should have a comprehensive dental examination. The dentist will assess the oral health, take impressions, and discuss the type of dentures best suited for the patient (complete or partial).
Duration of Procedure: The process of getting dentures typically spans several weeks, as it involves multiple visits for impressions, fittings, and adjustments. Each appointment may take about 30 minutes to an hour.
Recovery Time: Adapting to new dentures may take some time. Initially, patients might experience discomfort, increased salivation, or difficulty speaking and eating. Most people adjust within a few weeks, but follow-up appointments for adjustments may be necessary.
Estimated Cost: The cost of dentures can vary widely based on the type (complete or partial), materials used, and the complexity of the case. Prices can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Patients should consult their dentist for an accurate estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After receiving dentures, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial. Patients should clean their dentures daily and remove them at night. Regular dental check-ups are also important to ensure proper fit and function and to check the health of the gums.

Periodontal Treatment (Gum Treatment)
Purpose: Periodontal treatment aims to prevent, diagnose, and treat gum disease (periodontitis) and other conditions affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. This treatment helps to maintain gum health, prevent tooth loss, and improve overall oral health.
Procedure: The procedure for periodontal treatment can vary based on the severity of the gum disease. Common treatments include scaling and root planing, where the dentist cleans the teeth above and below the gum line to remove plaque and tartar. In more severe cases, surgical options may be necessary to reduce gum pockets or regenerate lost tissue.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Periodontal treatment is usually performed in a dental office as an outpatient procedure. Some surgical treatments may require a longer visit, but no overnight hospital stay is needed.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Patients can return home after each appointment.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area being treated, especially during more invasive procedures. Sedation may also be offered for anxious patients.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can generally travel immediately after periodontal treatment. However, they should avoid strenuous activities for the rest of the day, especially after surgical procedures.
Preparation Before Procedure: Prior to periodontal treatment, patients may undergo a thorough dental examination and may need X-rays to assess the extent of gum disease. It is important to discuss any medications and medical conditions with the dentist.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of periodontal treatment can vary widely based on the specific procedure and the severity of the condition. Scaling and root planing typically take about 1 to 2 hours, while surgical treatments may take longer.
Recovery Time: Recovery time after periodontal treatment varies depending on the type of procedure performed. Patients may experience some discomfort, swelling, or bleeding, which usually resolves within a few days. Full healing may take a few weeks, particularly after surgical treatments.
Estimated Cost: The cost of periodontal treatment can vary widely depending on the severity of the disease and the specific procedures required. It may range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Patients should consult their dentist for a detailed estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After periodontal treatment, it’s important for patients to follow the dentist’s instructions for care, which may include maintaining good oral hygiene, attending follow-up appointments, and possibly making lifestyle changes to improve gum health. Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring progress.
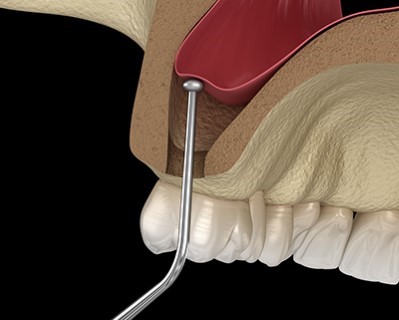
Sinus Lift
Purpose: A sinus lift, or sinus augmentation, is a surgical procedure performed to increase the amount of bone in the upper jaw, specifically in the area of the molars and premolars. This procedure is often necessary when there is insufficient bone height to support dental implants, usually due to bone loss caused by periodontal disease or tooth loss.
Procedure: During a sinus lift, the dentist or oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum tissue to expose the bone. A small window is created in the bone, and the sinus membrane is gently lifted. Bone graft material is then placed in the area to promote new bone growth. The gum tissue is then stitched back into place, and the area is allowed to heal.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: A sinus lift is usually performed in a dental office or oral surgery center as an outpatient procedure.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Patients can return home after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is commonly used during a sinus lift. In some cases, sedation may also be offered to help patients feel more comfortable.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can typically travel home immediately after the procedure. It’s advisable to avoid strenuous activities for several days to promote healing.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before undergoing a sinus lift, patients usually receive a comprehensive dental examination, including X-rays or 3D imaging to assess bone levels and sinus anatomy. Discussing any medications or health conditions with the dentist is important.
Duration of Procedure: The sinus lift procedure typically takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery Time: Recovery time can vary, but patients may experience swelling, discomfort, or minor bleeding for a few days. Complete healing may take several months before dental implants can be placed.
Estimated Cost: The cost of a sinus lift can vary widely based on the complexity of the procedure and the geographic location. It typically ranges from a few hundred to a couple of thousand dollars. Patients should consult their dentist for an accurate estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After a sinus lift, patients should follow their dentist’s instructions for care, which may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding certain activities, and maintaining good oral hygiene. Follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing.
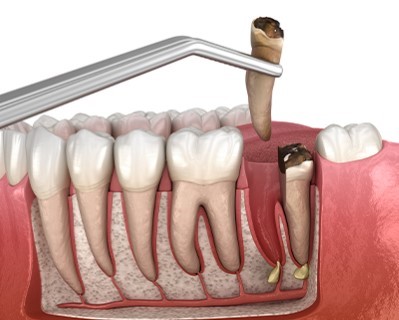
Root Extraction
- Purpose: Removes the tip of the tooth root and seals the root canal to treat persistent infection.
- Procedure: An incision is made in the gum tissue to access and remove the infected root tip.
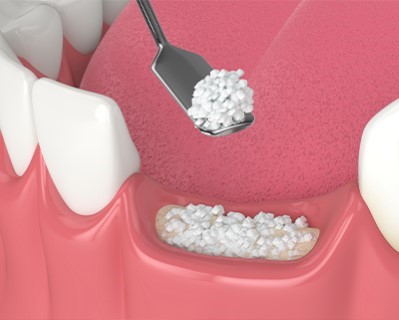
Bone Grafting
Purpose: Bone grafting is a surgical procedure used to replace or augment missing bone in the jaw or other areas of the body. It is often performed to provide a solid foundation for dental implants or to repair bone defects caused by trauma, disease, or developmental issues.
Procedure: During a bone grafting procedure, the surgeon makes an incision to access the area of missing bone. Bone graft material, which can be sourced from the patient (autograft), a donor (allograft), or synthetic materials, is placed in the area to stimulate new bone growth. The incision is then closed, and the area is allowed to heal.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Bone grafting is typically performed in a dental office or surgical center as an outpatient procedure, although some complex cases may require a short hospital stay.
Duration of Hospital Stay: Generally, no hospital stay is required for simple bone grafting. Patients can return home the same day.
Type of Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is commonly used during the procedure. Sedation may also be offered to help patients relax.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can usually travel home immediately after the procedure. It's advisable to avoid strenuous activities for a few days to facilitate healing.
Preparation Before Procedure: Prior to bone grafting, patients undergo a thorough evaluation, including X-rays or imaging studies, to assess the area and determine the appropriate grafting technique. Discussing any medications or medical conditions with the surgeon is essential.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of the bone grafting procedure can vary but typically takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
Recovery Time: Recovery time can vary based on the type of graft and the individual's healing process. Patients may experience swelling, discomfort, or bruising, which usually resolves within a week. Complete healing and integration of the graft can take several months.
Estimated Cost: The cost of bone grafting varies widely based on factors such as the type of graft used and the complexity of the procedure. It can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. Patients should consult their dentist or oral surgeon for an accurate estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After bone grafting, patients should follow their surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding certain foods, and maintaining good oral hygiene. Follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the healing process.
Pediatric Dentistry
Purpose: Pediatric dentistry focuses on the oral health of infants, children, and adolescents. It aims to provide preventive and therapeutic care for the unique dental needs of children, including the management of dental growth, development, and early dental issues like cavities, gum diseases, and misaligned teeth.
Procedure: Pediatric dental care includes a variety of treatments, such as regular dental cleanings, fluoride treatments, dental sealants, cavity fillings, and treatment of oral infections. Pediatric dentists also monitor the development of a child's teeth and jaw, offering early intervention in cases of misaligned teeth or bite problems.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Most pediatric dental procedures are performed in a dentist's office on an outpatient basis. Complex cases or surgeries may require treatment in a hospital setting.
Duration of Hospital Stay: Generally, pediatric dental procedures do not require a hospital stay. Children can return home the same day after treatment.
Type of Anesthesia: Pediatric dental procedures often use local anesthesia for cavity fillings or other minor treatments. For more complex procedures or anxious children, sedation or general anesthesia may be used to ensure comfort and safety.
Travel After Procedure: After most pediatric dental procedures, children can return home immediately. However, for treatments involving sedation or anesthesia, rest and supervision are recommended for the remainder of the day.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before pediatric dental procedures, parents should discuss their child's medical history and any medications with the dentist. It’s important to follow any instructions provided by the dentist, especially when sedation or anesthesia is involved.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of pediatric dental procedures varies based on the type of treatment. Routine cleanings may take 30 minutes, while fillings or extractions may take up to an hour.
Recovery Time: Recovery time after pediatric dental procedures is generally short. Children may experience some discomfort or numbness after fillings or extractions, but these symptoms usually resolve within a few hours to a day.
Estimated Cost: The cost of pediatric dental care depends on the type of treatment, the complexity of the procedure, and the geographic location. Basic treatments like cleanings and fluoride treatments are generally affordable, while more complex treatments like fillings or orthodontics may cost more. Parents should consult their dentist for a detailed estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After pediatric dental procedures, parents should ensure that children follow proper oral hygiene routines, such as brushing and flossing regularly. Avoiding hard or sticky foods and attending follow-up appointments as needed is also important for maintaining good oral health.
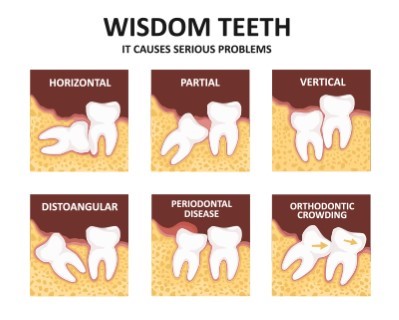
Wisdom Teeth Removal
Purpose: Wisdom teeth removal, or third molar extraction, is a common surgical procedure to remove one or more of the four wisdom teeth. These teeth are the last to emerge, often causing crowding, impaction, or infection, which can lead to pain, swelling, or damage to adjacent teeth. Removing them can prevent or address these issues.
Procedure: During the procedure, the oral surgeon or dentist makes an incision in the gum to access the tooth. In some cases, the tooth may need to be broken into smaller pieces for easier removal. Once the tooth is extracted, the incision is closed with stitches, and the area is packed with gauze to help stop any bleeding.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Wisdom teeth removal is typically done in a dental office or oral surgery center on an outpatient basis.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. The patient can go home after the procedure, usually within a few hours.
Type of Anesthesia: The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the extraction and the patient’s comfort level.
Travel After Procedure: Patients are advised to arrange for someone to drive them home after the procedure, especially if sedation or general anesthesia is used. It’s recommended to rest and avoid physical exertion for a few days.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before wisdom teeth removal, the dentist or oral surgeon will conduct a thorough examination, including X-rays, to assess the position and condition of the teeth. Patients should inform the dentist of any medications they are taking and follow pre-surgery instructions, such as fasting if general anesthesia is planned.
Duration of Procedure: The removal of wisdom teeth usually takes about 45 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the number of teeth being removed and the complexity of the procedure.
Recovery Time: Recovery from wisdom teeth removal can take a few days to a week. Patients may experience swelling, bruising, or discomfort for the first few days, with full healing taking several weeks. Pain medications and ice packs are often recommended to manage symptoms.
Estimated Cost: The cost of wisdom teeth removal varies depending on factors like the number of teeth being removed, the complexity of the surgery, and the type of anesthesia used. Costs can range around a few hundred dollars. It’s important to consult with the dentist or surgeon for a more accurate estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After wisdom teeth removal, patients should follow the dentist’s post-operative care instructions, which may include avoiding hard or chewy foods, using ice packs for swelling, taking prescribed medications, and gently rinsing the mouth with salt water. Follow-up visits may be required to remove stitches and check the healing process.
_20240719135645661265__0.webp)
Smile Design (Hollywood Smile)
Purpose: Smile design, also known as smile makeover, is a cosmetic dental treatment aimed at improving the appearance of a person’s smile. It combines several dental procedures to enhance the shape, color, alignment, and overall aesthetics of teeth and gums, giving patients a more harmonious and attractive smile.
Procedure: Smile design typically involves a combination of cosmetic treatments such as teeth whitening, veneers, crowns, orthodontics (braces or clear aligners), dental bonding, gum contouring, and implants. The specific procedures will vary depending on the patient’s needs and the desired outcome. Advanced digital technology may be used to design and preview the expected results before treatment.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: Smile design procedures are performed in a dental clinic on an outpatient basis.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. Most procedures can be completed during office visits, though more extensive work may require multiple appointments over several weeks or months.
Type of Anesthesia: Depending on the specific procedures involved, local anesthesia may be used for treatments like gum contouring or dental implants. Most smile design treatments, such as veneers or whitening, require no or minimal anesthesia.
Travel After Procedure: Patients can usually travel after smile design treatments. However, if invasive procedures like implants or gum surgery are involved, it’s recommended to rest for a few days and avoid strenuous activities.
Preparation Before Procedure: Before starting a smile design, the dentist will assess the patient’s dental health, take X-rays, and perform digital scans or molds of the teeth. Patients should discuss their aesthetic goals and follow any pre-procedure instructions provided by the dentist.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of smile design varies greatly based on the number of procedures involved. Simple treatments like whitening can take about 1 hour, while more comprehensive makeovers involving orthodontics or implants may take several months to complete.
Recovery Time: Recovery time depends on the specific treatments performed. Whitening and veneers typically require little to no downtime, while recovery from implants or gum contouring may take a few days to a couple of weeks.
Estimated Cost: The cost of a smile design varies widely based on the treatments involved, the complexity of the case, and the geographic location of the clinic. A basic smile design with whitening and veneers may be relatively affordable, while more extensive work including implants or orthodontics can be more expensive. Consultation with the dentist is recommended to get a personalized estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After smile design treatments, patients should maintain proper oral hygiene by brushing, flossing, and visiting the dentist regularly. Specific instructions may be provided for aftercare, especially if dental implants or gum treatments were involved. Regular check-ups will help maintain the results of the smile makeover.

Orthognathic Surgery
- Purpose: Corrects jaw abnormalities to improve function and appearance.
- Procedure: Surgical repositioning of the jaw bones.
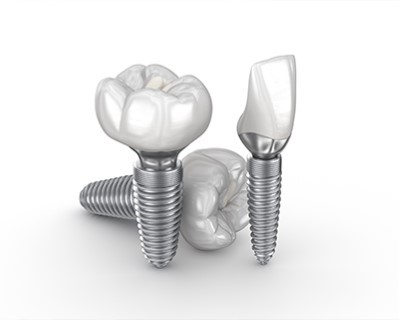
3D Printed Dental Implants
Purpose: 3D printed dental implants are a cutting-edge solution used to replace missing teeth. This technology allows for highly customized implants that match the patient’s specific anatomy and oral structure, improving the fit, functionality, and appearance of the replacement tooth. The use of 3D printing in implantology enhances precision, reduces treatment time, and can improve long-term outcomes.
Procedure: The process begins with a digital scan of the patient's mouth, creating a precise 3D model of the jaw and surrounding teeth. Using this model, a customized implant is designed to perfectly fit the patient’s bone structure. The implant is then fabricated using biocompatible materials, often titanium or ceramic, through 3D printing technology. Once printed, the implant is surgically placed into the jawbone, similar to traditional implants.
Hospital/Clinic Stay: The procedure is performed in a dental clinic or specialized oral surgery center.
Duration of Hospital Stay: No hospital stay is required. The patient can return home after the procedure.
Type of Anesthesia: The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia. However, in more complex cases or for patients who experience anxiety, sedation or general anesthesia may be used.
Travel After Procedure: Most patients are advised to rest after the procedure but can travel as soon as they feel comfortable. Long-distance travel is generally discouraged immediately after the surgery.
Preparation Before Procedure: Preparation involves a comprehensive oral examination, including digital scans, X-rays, and sometimes CT scans, to ensure proper bone structure for the implant. Patients may be asked to follow specific dietary restrictions or stop certain medications before the procedure.
Duration of Procedure: The duration of the surgery varies but typically takes between 1 to 2 hours, depending on the number of implants and the complexity of the case. The process of designing and 3D printing the implant occurs prior to surgery and can take a few days to a couple of weeks.
Recovery Time: Recovery from the surgical placement of 3D printed implants can take several days to a week for initial healing. Full integration of the implant into the jawbone, known as osseointegration, may take 3 to 6 months. During this time, a temporary crown may be placed until the permanent restoration is ready.
Estimated Cost: The cost of 3D printed dental implants can be higher than traditional implants due to the advanced technology and customization involved. The price varies depending on the number of implants, materials used, and the clinic's location. A consultation with the dentist or surgeon is necessary to get an accurate cost estimate.
Post-Procedure Care: After receiving the implant, patients should follow the dentist's post-operative care instructions, which may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding certain foods, and maintaining excellent oral hygiene. Regular follow-up appointments will be required to monitor healing and ensure the implant is integrating properly.
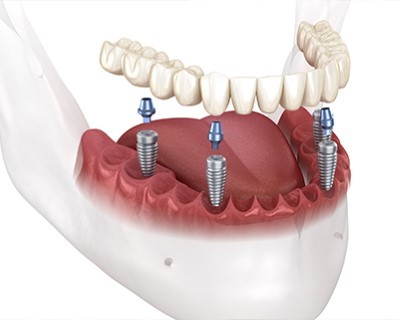
All-on-Four Treatment
- Purpose: Provides a full arch of teeth using only four dental implants to support a fixed prosthesis.
- Procedure: Four dental implants are strategically placed in the jaw, two at the front and two at the back, at specific angles to maximize bone use and support a fixed bridge.
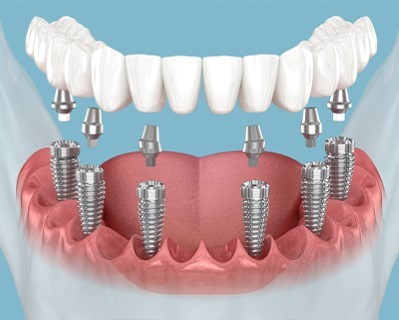
All-on-Six Treatment
- Purpose: Provides a more stable and secure full arch of teeth using six dental implants.
- Procedure: Six dental implants are placed in the jaw to support a fixed prosthesis, offering enhanced stability and distribution of bite force compared to the All-on-Four method.
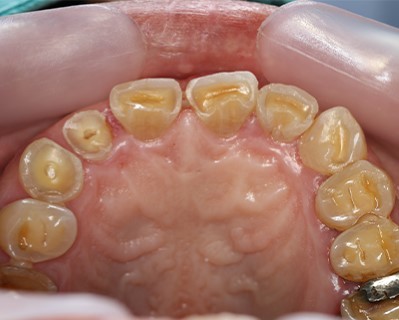
Bruxism Treatment
- Purpose: Reduces the effects of teeth grinding and clenching to prevent tooth damage and alleviate associated pain.
- Procedure: Various approaches including behavioral therapies, medication, and dental devices may be used. Behavioral therapies focus on stress management techniques, while medications like muscle relaxants or Botox can reduce muscle activity. Dental devices such as night guards protect teeth from grinding during sleep.
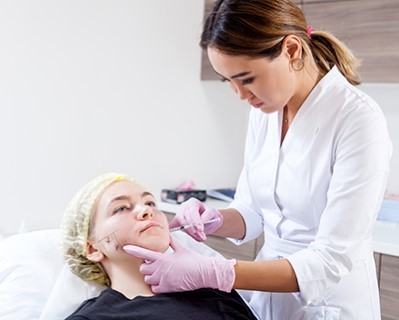
Masseter Botox
- Purpose: Relieves jaw tension and pain associated with bruxism by relaxing the masseter muscle.
- Procedure: Botox injections are administered into the masseter muscle, reducing its activity and helping to alleviate the symptoms of bruxism. The effects typically last for 3 to 6 months, and the procedure can be repeated as necessary.
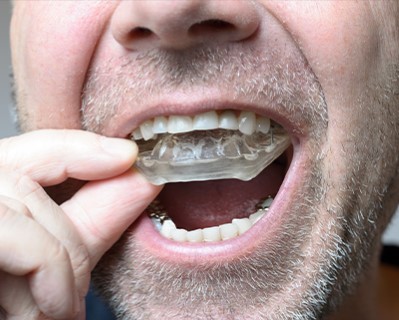
Night Guard
- Purpose: Protects teeth from the damaging effects of grinding and clenching during sleep.
- Procedure: A custom-fitted dental night guard is created to fit the patient's teeth, providing a barrier between the upper and lower teeth. This helps to prevent tooth damage, reduce jaw strain, and alleviate symptoms associated with bruxism.
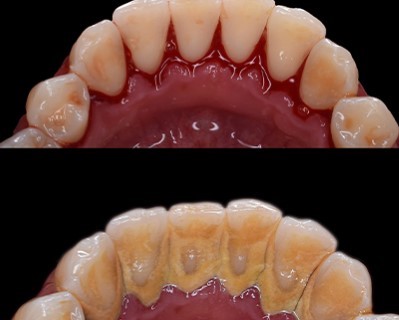
Deep Cleaning
Purpose: Treats gum disease and prevents further progression by removing plaque and tartar below the gumline.
Procedure:
- Scaling and Root Planing: Plaque and tartar are removed from teeth surfaces and below the gumline, and the roots are smoothed to help gums reattach and prevent further buildup.
